Introduction
Many years ago, when Visual Basic 6 was a way to simply develop Windows Graphic User Interface (GUI) programs (now known as apps), I developed a PC Time Sync application, synchronizing PC time to a GPS serial NMEA RMC (Recommended Minimum specific GPS data) sentence, for digital communications protocols e.g. WSJT for tropo and EME.
It is now five years since the increasing noise in my residential area caused me to abandon 2m EME with a plan of moving to 70cm. Three years ago, the 70 cm project stalled due to my lack of confidence to build a high performance four bay crossed Yagi for coherent reception of vertical and horizontal polarization by MAP65. Recent acquisition of an 80cm SeaTel Satellite TV dish and a 2m solid aluminium dish for 3 and 23 cm respectively, rekindled the motivation.
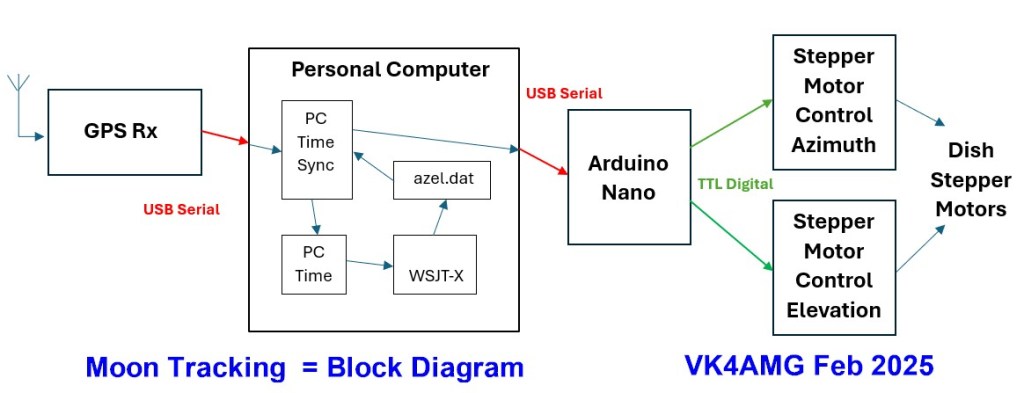
After investigating alternatives for moon tracking, a system (see block diagram below) to steer the stepper motors and rotators for the three EME bands was developed. The system uses the WSJT azel.dat tracking data and passes tracking commands via the GPS disciplined 10MHz reference GPSD-2 module by VK4AMG (see https://brisbaneradiosociety.net/10-mhz-reference-by-vk4amg/).
Time Sync and Tracking Application
While Microsoft still support VB6 application in Windows 10 and Windows 11, the support (and the installation of the VB6 IDE) for development is prohibited. This limitation complicated the development and testing of the software components of the project. Development and testing were split over three computers. A five-year-old PC, setup for Windows XP and Visual Studio 6, allowed revision of my PC Time Sync program to include extraction of tracking data from WSJT and serial export of data to an Arduino Nano controlling stepper motors (for the small dish) and for rotators for the 70cm Yagi array and 2m dish.
The original PC Time Sync program is described on PC Time Sync Application and as a .pdf copy.
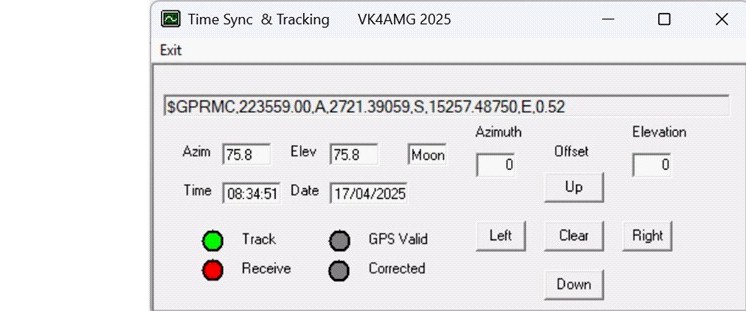
The revised application reads and displays the tracking data from WSJT (C:\WSJT\tracking\azel.dat). Both the moon and sun position may be tracked. Offsets may be applied by scroll bars and push buttons on the GUI. The tracking commands are transmitted by the USB serial port from which the GPS NMEA sentences are received. The GPSD-2 GPS Disciplined 10MHz reference module is revised (hardware only) to pass the tracking commands to the Android Nano processor controlling the stepper motors or rotators. The commands are passed in a format “W az.a el.e <CRLF>” where az.e is a single digit floating point number for azimuth and el.e is a single digit floating point number for elevation. “W 0.0 0.0 <CRLF>” is invalid and forces a stop command. A command less than 10 degrees elevation triggers a park to a position set in the rotator controller processor.
The original functions of PC time sync and GPS NMEA RMC pseudo-RS232 for IC9700 and similar radios (for time and position) together with status indication of serial receive from GPS, valid GPS, correction and tracking are provided.
SeaTel Marine Satellite TV Dish
A surplus SeaTel Marine Satellite TV system became available locally. The carbon fibre 32” dish was setup for Ku band satellite operation on a ship or yachts, LNB with circular waveguide to Cassegrain reflector, solid state gyros for roll and pitch correction, signal strength metering for tracking, and motor control. The dish is fitted with stepper motors, well-engineered belt drives and pivots, and limit switches for azimuth, elevation, and polarization control.
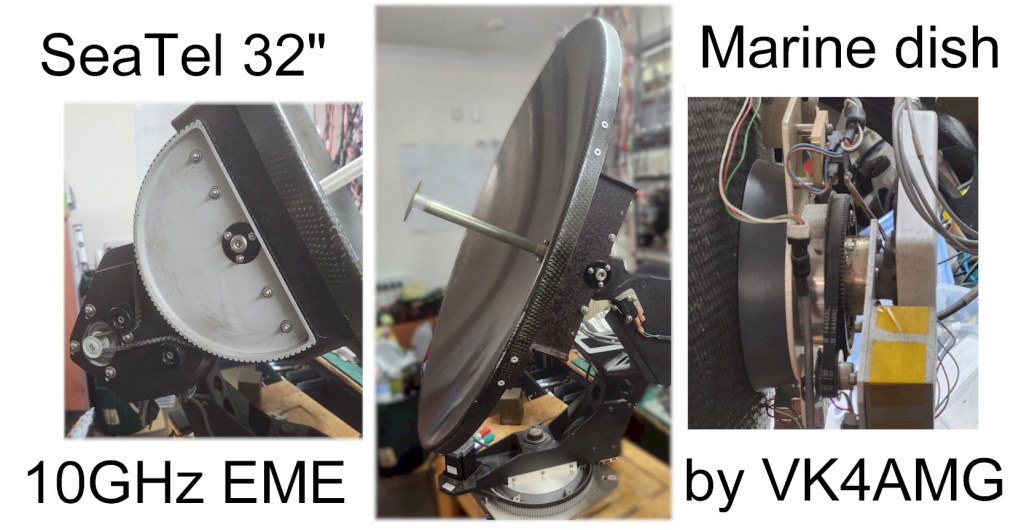

As my first meeting with controlling stepper motors, I chose a TB6600HG stepper motor controllers as the controlling processor, Arduino Nano, interface is simple (Direction, Enable, and a pulse for each step. This controller also has a built-in current limit and up to 6400 steps/rev capability. The latter provides a smooth, low vibration, but good stepping speed for this project.
The Arduino software is novel as the stepping is executed by timer1 interrupt service routine under control by flags from the main loop. The latter handles the serial communication, command parsing, limit checking, timeouts, and control of timer execution.
The Arduino software initializes the dish position by rotating the dish to a limit switch and then rotating to 180 degrees (North) position. During the latter the elevation is stepped down until its limit switch and then moved to its home of horizontal. See https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tpw759Ycmjs
The azimuth and elevation are then tracked by motor step count. With 30+ steps per degree, the step size is less than 0.03 degree. To maintain the accuracy of the dish position and hysteresis is applied to the Arduino control algorithm. Position accuracy is better than 0.1 degree, the resolution of the WSJT data.
An hour test has been time lapse recorded and is available as a video at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z_IkyuJAGeo .
Windows Application – Az El Serial Commands
TimeSync and Tracking Application – readme.doc explains the PC application, its installation, and operation. Application reads WSJT az.el.dat file and outputs serial commands for external stepper motor and rotator controllers.
Stepper Motor Controller
Controller setup, design notes, and Arduino software An Arduino Nano controls the SeaTel stepper motors for azimuth and elevation via two TB6600HG stepper motor controllers.
Yaesu Rotator Controller
Rotator setup, design notes, and Arduino software An Arduino Nano controls a Yaesu G5500 or Kenpro azimuth / elevation rotator.